What is Male Infertility?
What is Male Infertility?
Understanding Male Infertility
Male infertility occurs when a man has a reduced ability to impregnate a woman. It is a significant contributor to couples’ struggles with conception, accounting for around 30-40% of all infertility cases. Male infertility is often related to problems with sperm production, quality, or the delivery of sperm.
Common Causes of Male Infertility
- Low Sperm Count (Oligospermia): When the semen contains fewer sperm than normal, making it harder to achieve conception. A sperm count of fewer than 15 million sperm per milliliter is considered low.
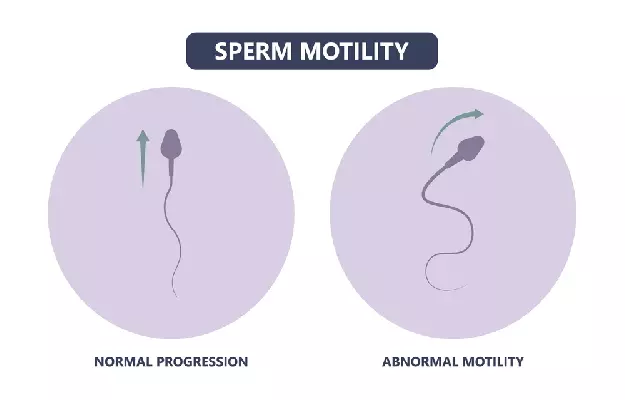
- Poor Sperm Motility: Refers to the sperm’s ability to swim. If sperm can’t swim well, they may have trouble reaching and fertilizing the egg.
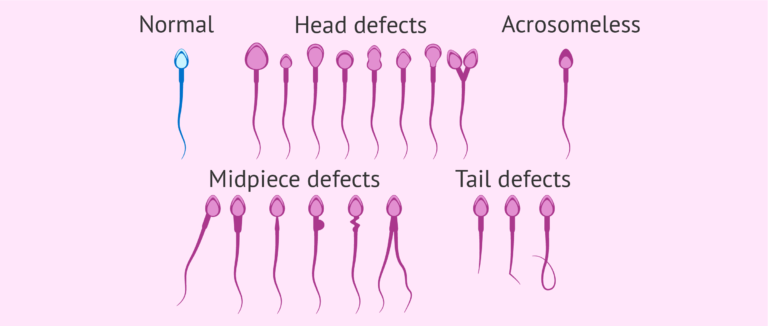
- Abnormal Sperm Morphology: The shape and structure of sperm can affect their ability to penetrate an egg. A high percentage of abnormally shaped sperm can reduce fertility.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Testosterone and other hormones play an essential role in sperm production. Imbalances in these hormones can lead to reduced fertility.
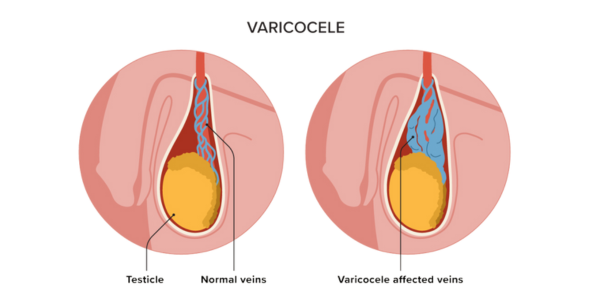
- Varicocele: A condition where the veins within the scrotum become enlarged, potentially impacting sperm production.
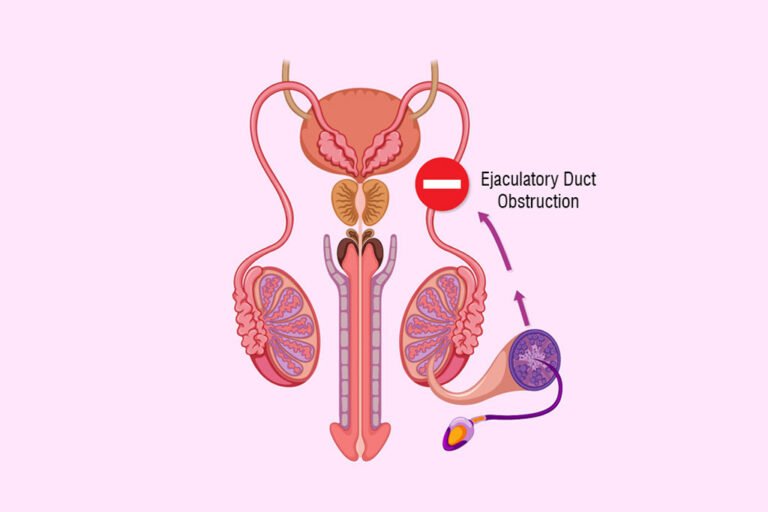
- Ejaculatory Issues: Problems such as retrograde ejaculation, where semen enters the bladder instead of exiting through the penis, can prevent sperm from reaching the egg.
- Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
- Smoking and Alcohol: These can decrease sperm count and quality.
- Exposure to Toxins: Chemicals, pesticides, and prolonged exposure to heat (such as hot tubs or saunas) can negatively affect sperm production.
- Stress and Obesity: High-stress levels and being overweight can interfere with sperm production and overall reproductive health.
- Diagnosis and Testing
Treatment Options for Male Infertility
Male infertility is typically diagnosed through a series of tests:
Identifies genetic disorders or chromosomal abnormalities that may be contributing to infertility, which can provide insights into the cause and guide treatment options.
Male infertility is typically diagnosed through a series of tests:
- Semen Analysis: Evaluates the health, quantity, and movement of sperm.
- Hormonal Testing: Measures levels of testosterone and other hormones.
- Scrotal Ultrasound: Can identify structural abnormalities such as varicoceles.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Improving diet, exercise, and reducing exposure to toxins can enhance sperm quality.
- Medications: Hormonal treatments may help regulate sperm production.
- Surgical Procedures: For correcting blockages or repairing varicoceles.
- ART Methods: Techniques like IUI or IVF with ICSI (Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection) can help overcome severe cases of male infertility.
You’re Not Alone on This Journey
Infertility can be an emotional challenge, but support is here. Join our support groups, explore counseling options, or speak with a specialist to help navigate the stress of your journey to parenthood.